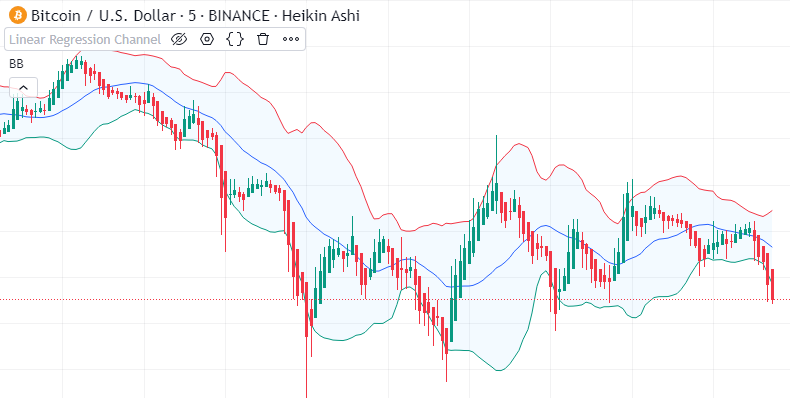
Introduction to Bollinger Bands
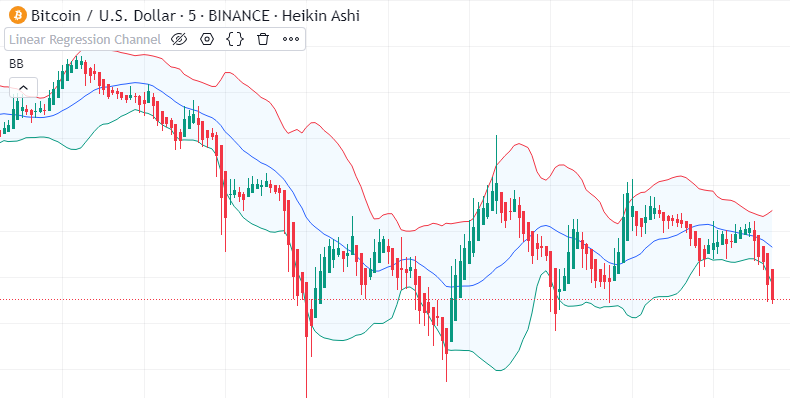
Introduction to Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands are a well-known tool for technical analysis that traders use to evaluate the volatility and potential price changes of a financial instrument. John Bollinger developed this indicator in the 1980s. It helps traders spot when the market is overbought or oversold giving them useful insights to make smart trading choices.
What are Bollinger Bands?
Bollinger Bands have three lines: the middle band, the upper band, and the lower band. The middle band is usually a simple moving average (SMA) set at 20 periods. The upper and lower bands are worked out by adding and taking away a standard deviation from the middle band. This creates a range that changes with market ups and downs.
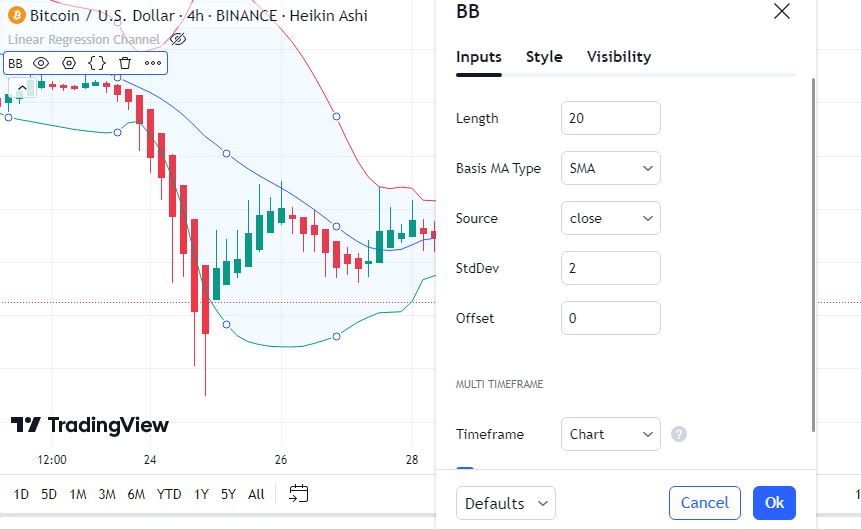
How to Work Out Bollinger Bands
To work out Bollinger Bands, follow these steps:
- Middle Band (SMA): Work out the 20-period simple moving average of the asset’s closing prices.
- Upper Band: Add two standard deviations to the middle band.
- Lower Band: Take away two standard deviations from the middle band.
These calculations give a picture of how prices move and how unstable they are.
Understanding Bollinger Bands
You can use Bollinger Bands in different ways to help with trading plans:
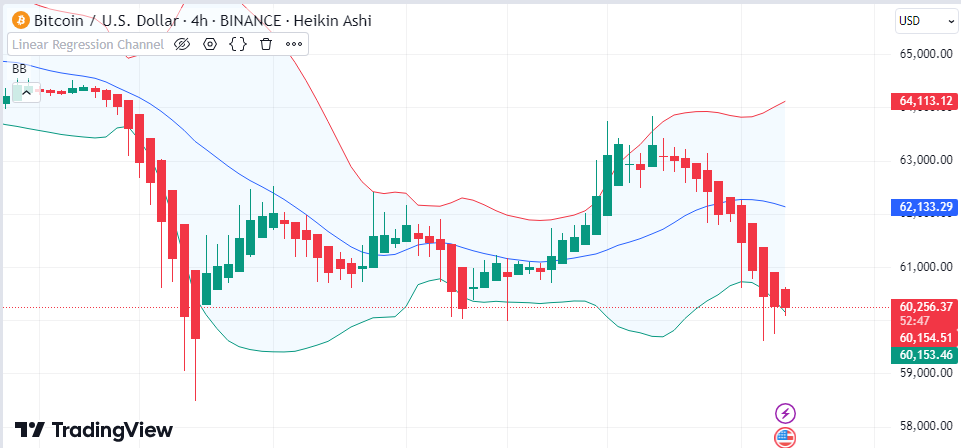
- Too High or Too Low Prices: When the price gets close to the top band, the asset might be too expensive. On the flip side when the price nears the bottom band, it might be too cheap.
- Trend Changes: If the price breaks above the top band or below the bottom band, it could mean the trend might change.
- Signs of Instability: When the bands get closer, it suggests low instability and a possible big move. When they spread out, it shows high instability.
Trading Plans Using Bollinger Bands
Here are a few common trading tactics that use Bollinger Bands:
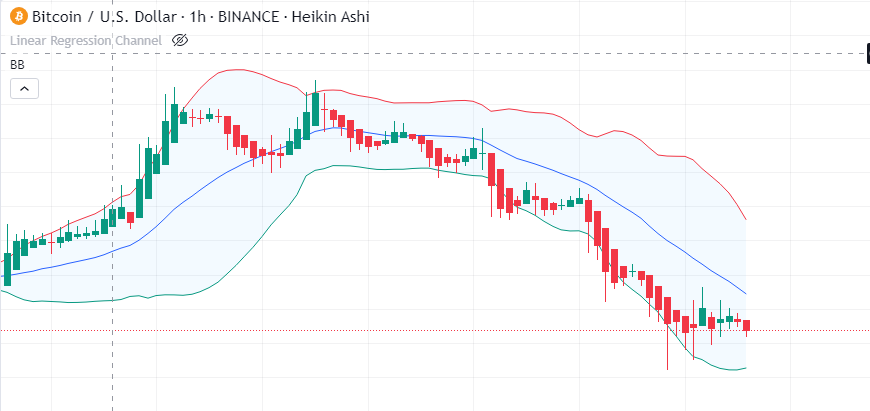
1. Bollinger Band Squeeze
The Bollinger Band Squeeze tactic spots times of low volatility. When the bands get closer, it signals a possible breakout. Traders look for the price to move above or below the bands to start a trade in the breakout’s direction.
2. Bollinger Band Bounce
The Bollinger Band Bounce tactic involves trading when the price hits the top or bottom band and then goes back toward the middle band. This tactic works well in markets that range where prices move between support and resistance levels.
3. Bollinger Bands and RSI
Using Bollinger Bands with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) has an impact on trading signals. The price touching the upper band and an overbought RSI might signal a good time to sell. On the other hand, the price touching the lower band and an oversold RSI could point to a good time to buy.
Advantages of Bollinger Bands
- Dynamic Range: Bollinger Bands adapt to market conditions giving a more exact picture of volatility.
- Versatility: Traders can use them on different financial products, like stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
- Easy to Use: People find Bollinger Bands simple to grasp and add to their trading plans.
Limitations of Bollinger Bands
- False Signals: Bollinger Bands can give off incorrect signals when markets have low volatility or are trending.
- Lagging Indicator: Since Bollinger Bands lag behind price action, they might not always provide the best timing for entering or exiting trades.
To wrap up
Bollinger Bands are a useful tool for traders who want to understand market volatility and spot potential trading chances. By adding Bollinger Bands to your technical analysis toolkit, you can boost your trading strategies and make better-informed choices. Keep in mind that it’s best to use Bollinger Bands alongside other indicators and analysis methods to improve accuracy and lower the risk of false signals.
Questions people often ask about Bollinger Bands
1. What is the best period setting for Bollinger Bands?
Traders use a 20-period moving average with two standard deviations. But they can change these settings to match their trading approach and the asset they’re looking at.
2. Can Bollinger Bands be used for day trading?
Bollinger Bands work well for day trading. They help traders spot quick price changes and how jumpy the market is.
3. How do Bollinger Bands compare to other volatility indicators?
Bollinger Bands stand out because they adapt on their own to market conditions. This is different from indicators like the Keltner Channel or the Donchian Channel, which have fixed widths.
4. Do Bollinger Bands work well in trending markets?
Bollinger Bands might not be as helpful in strong trending markets, as they could give wrong signals. It’s better to use them along with indicators that follow trends.
By grasping and using Bollinger Bands, traders can better understand how markets work and get better results from their trades.
Common Questions about Trading Indicators
1. What are the Four Main Types of Trading Indicators?
All technical indicators, no matter how complex show one or a mix of four key things:
- Volume
- Trend
- Volatility
- Momentum
2. How Can You Apply Indicators to Trading?
The indicator’s position in relation to zero plays a key role in figuring out which signals to follow. For example when the indicator sits above zero, traders should watch for the MACD to cross above the signal line as a buy signal. On the other hand, if the MACD falls below zero, a cross under the signal line might suggest a possible short trade.
3. How to Pick a Useful Indicator?
Pick an indicator with a pH range that matches the pH of the specific reaction. Take the titration of a strong acid with a strong base as an example. The pH changes from 3 to 11, so phenolphthalein (with a range from pH 8-10) works well as an indicator. Also, think about the color change aspect.
4. How to Analyze a Trading Market?
To start technical analysis, follow these seven steps:
- Set up a trading account.
- Put money in.
- Pick the markets you want to trade.
- Pull up the market’s chart.
- Figure out what’s happening in the market right now.
- Look at patterns and indicators to guess where the market might go next.
5. Which Chart is Best for Trading?
Active traders prefer candlestick charts over other types. These charts combine the good points of line and bar charts showing how time and value affect each other. Each candlestick stands for a specific time period and shows the opening, closing, high, and low prices.
6. What is the Best Self-Indicator?
Potassium permanganate serves as a great example of a self-indicator in redox titrations. It changes color when the reaction finishes.
7. How to Read Stock Charts?
- Day’s Open: The stock price when trading begins for the day.
- Day’s Close: The stock price when trading ends for the day.
- Day’s High: The peak price the stock hits during the day.
- Day’s Low: The bottom price the stock reaches during the day.
8. Which Indicator Shows Buy and Sell Signals?
The stochastic indicator goes from 0 to 100. A reading over 80 points to an overbought security (sell signal), while a reading under 20 suggests an oversold security (buy signal).
9. What is the Best Indicator for Trading?
Key technical indicators for day trading include the RSI, Williams Percent Range, and MACD. These indicators point out overbought and oversold levels, helping predict future price changes based on past performance.
10. How to Confirm Trend Direction?
Traders confirm trend direction by linking a series of highs and lows. They spot an uptrend by connecting rising low points, while a downtrend shows up when they link falling high points. Markets without a clear direction or flat trends stand out due to their lack of clear high and low connections.f clear high and low connections.
Join More Airdrop:
- Pi Network Airdrop
- AZCoiner Airdrop
- Satoshi Airdrop
- Grass Airdrop
- Athene Network Airdrop
- Celia Exchange Airdrop
- Bee Network Airdrop